 Anyone with symptoms should be tested, wherever possible. People who do not have symptoms, but have had close contact with someone who is, or may be, infected may also consider testing – contact local health officials and follow their guidance.
Anyone with symptoms should be tested, wherever possible. People who do not have symptoms, but have had close contact with someone who is, or may be, infected may also consider testing – contact local health officials and follow their guidance.
While a person is waiting for test results, they should remain isolated from others. Where testing capacity is limited, tests should first be done for those at higher risk of infection, such as health workers and those at higher risk of severe illness such as older people, especially those living in seniors’ residences or long-term care facilities.
What test should I get to see if I have Covid-19?
In most situations, a molecular test is used to detect SARS-CoV-2 and confirm infection. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the most commonly used molecular test. Samples are collected from the nose and/or throat with a swab. Molecular tests detect virus in the sample by amplifying viral genetic material to detectable levels. For this reason, a molecular test is used to confirm an active infection, usually within a few days of exposure and around the time that symptoms may begin.
What is the difference between isolation and quarantine?
Both isolation and quarantine are methods of preventing the spread of Covid-19.
Quarantine is used for anyone who is a contact of someone infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes Covid-19, whether the infected person has symptoms or not. Quarantine means that you remain separated from others because you have been exposed to the virus and you may be infected and can take place in a designated facility or at home. For Covid-19, this means staying in the facility or at home for 14 days.
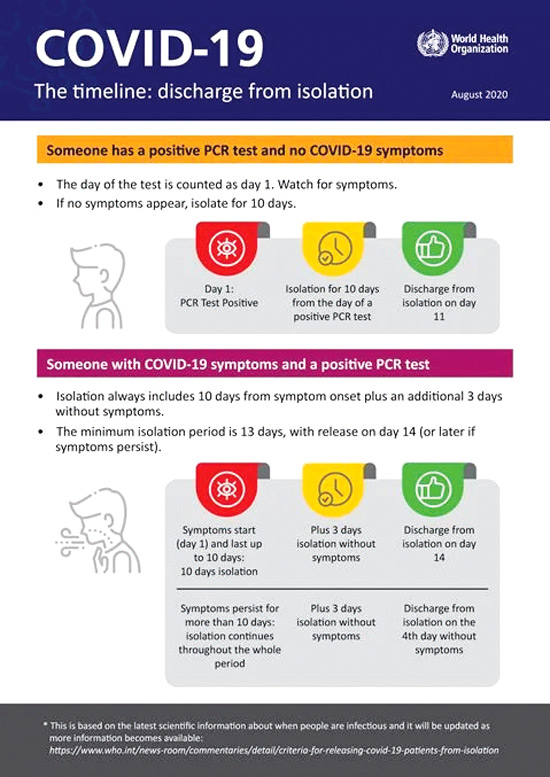
Isolation is used for people with Covid-19 symptoms or who have tested positive for the virus. Being in isolation means being separated from other people, ideally in a medically facility where you can receive clinical care. If isolation in a medical facility is not possible and you are not in a high risk group of developing severe disease, isolation can take place at home. If you have symptoms, you should remain in isolation for at least 10 days plus an additional 3 days without symptoms. If you are infected and do not develop symptoms, you should remain in isolation for 10 days from the time you test positive.
Are there treatments for Covid-19?
Scientists around the world are working to find and develop treatments for Covid-19.
Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid that can help reduce the length of time on a ventilator and save lives of patients with severe and critical illness.
Hydroxychloroquine has not been shown to offer any benefit for treatment of Covid-19.
The WHO does not recommend self-medication with any medicines, including antibiotics, as a prevention or cure for Covid-19. The WHO is coordinating efforts to develop treatments for Covid-19 and will continue to provide new information as it becomes available.
Are antibiotics effective in preventing or treating Covid-19?
Antibiotics do not work against viruses; they only work on bacterial infections. Covid-19 is caused by a virus, so antibiotics do not work. Antibiotics should not be used as a means of prevention or treatment of Covid-19.
In hospitals, physicians will sometimes use antibiotics to prevent or treat secondary bacterial infections which can be a complication of Covid-19 in severely ill patients. They should only be used as directed by a physician to treat a bacterial infection.
Source: World Health Organization
