 Osteoporosis is one of the commonest skeletal problems that weaken bone, making them fragile and more likely to break. It develops over the years often diagnosed when a fracture occurs. This could lead to many complications including long term pain.
Osteoporosis is one of the commonest skeletal problems that weaken bone, making them fragile and more likely to break. It develops over the years often diagnosed when a fracture occurs. This could lead to many complications including long term pain.
Bone is metabolically active. There is formation and resorption of bone. When the resorption exceeds formation it leads to Osteoporosis. The result is loose fragile bones, which leads to increased incidence of fractures. The disease can progress over time. In my experience bony fractures are much more common in the west than in this part of the world. It may be due to lack of sunlight and genetics. As a result fracture of the neck of femur is not uncommon among Caucasians.
Women are more prone to osteoporosis than men. This is due to the lack of hormones with increasing age.
Osteoporosis can be
1. Idiopathic
2. Secondary to other conditions such as
- Cancer
- Liver Impairment
- Coeliac Disease
- Gastric Surgery
- Coeliac Disease
High risk factors to develop Osteoporosis include
- Menopause (Hormonal imbalance)
- Steroid Therapy (long term)
- Family history
- Smoking and alcoholism
Pain in osteoporosis is caused by
- Vertebral crush fractures
- Back pain
- Facet Joint Arthropathy
- Sacroiliac disease
- Kyphosis - curvature of the spine
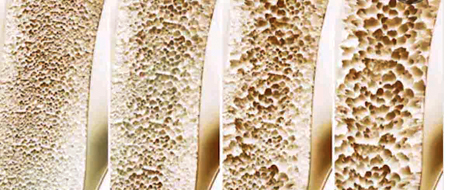
Different stages of Osteoporosis
Diagnosis
• Bone Density Scan - DEXA or DXA
• Bone X-ray for fractures
• CT Scan for fractures
• MRI Scan
DXA scan will convert the bone density into T and Z scores. T score compares the amount of bone compared to younger normal population. It will give a clue to the risk of bone fracture and how to plan the drug treatment. Z score compares the bone in relation to one’s own age group. This will give a clue to proceed with further investigations.
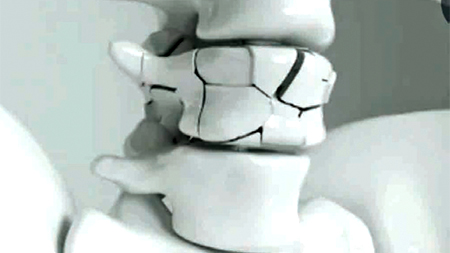
Fracture of vertebrae
Treatment
• Medications
- Biphisphonate –
Alendronate
- Calcitonin
- Vitamin D
- Hormone therapy – Oestrogen, Progesterone
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
- Parathyroid hormone analog
- Monoclonal antibody medication – Given as an injection under the skin every six months
• Stop smoking
• Limit alcohol
• Lifestyle changes to limit falls to prevent fractures
• Vertebroplasty for vertebral fractures – Cement is introduced to the fracture using X-ray guidance
•Kyphoplasty for vertebral fractures (balloon introduced into the fracture and a cavity is formed. Then the cement is injected into the cavity.
Vertebral fractures
Vertebral fractures can occur in any vertebrae from top to bottom in the spine. It is more common in the Lumbar region followed by the Thoracic region. Generally, it could be very painful across the level of the fracture. Diagnosis is by X-ray and CT scan. Adequate pain relief should be given to the patients to control pain. Pain medication should be given orally by the clock. Some fractures can be painless especially, the old ones.
Nerve blocks such as a dorsal root ganglion block can be tried.
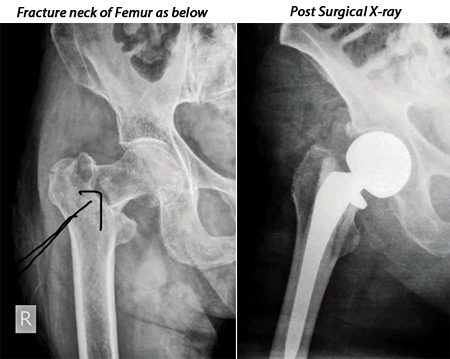
In the west fracture of the neck of femur is not uncommon in the older population, especially, in women. Mortality is around 30 percent. Fixing the fracture as soon as possible is the way forward.
Dr Senasinghe MBBS, Dip in Pain Med, FFARCS, FFPMCA, CCST(U.K)is a Consultant in pain medicine at the London Pain Management Centre, at No 31, Horton Place, Colombo 7, Sri Lanka.
Hotline 0767155716
