 Hyper mobility syndrome is due to very flexible joints in the body. Not all have very flexible joints keeping in mind that joints are flexible to a certain degree enabling movement. This leads to musculoskeletal pain. It occurs in the young age group (children and young adults). With advancing age generally the symptoms get better, may be due to less activity and slow pace. Increased flexibility of joints is due to lax ligaments and joints. This may be more common than we think. I have seen many patients with hyper mobility syndrome in the U.K. But during my short stint in Sri Lanka up to now I came across two young adults in their early 20s presenting with HMS.
Hyper mobility syndrome is due to very flexible joints in the body. Not all have very flexible joints keeping in mind that joints are flexible to a certain degree enabling movement. This leads to musculoskeletal pain. It occurs in the young age group (children and young adults). With advancing age generally the symptoms get better, may be due to less activity and slow pace. Increased flexibility of joints is due to lax ligaments and joints. This may be more common than we think. I have seen many patients with hyper mobility syndrome in the U.K. But during my short stint in Sri Lanka up to now I came across two young adults in their early 20s presenting with HMS.
Pain can lead to exhaustion towards the end of the day. Engaging in sports might be a painful experience. The joints of patients with the HMS move four times more than a normal person’s. Hence, the onset of pain and exhaustion.
Symptoms and signs of HMS
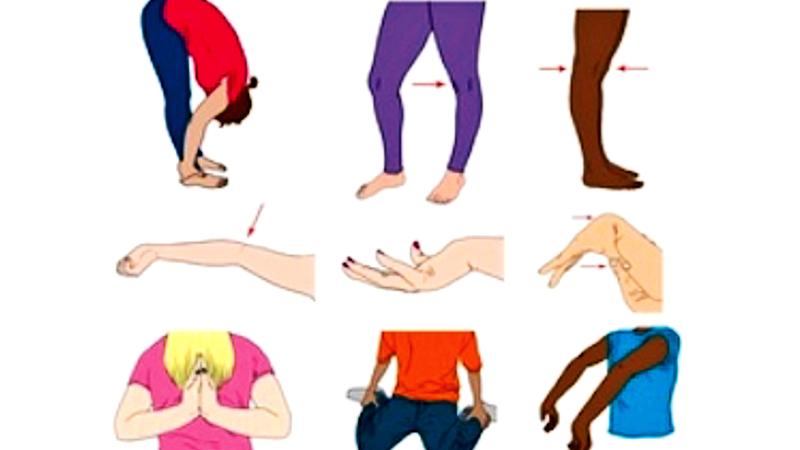
From the diagrams one can see the increased flexibility of the
body such as:
Touching the feet with the palm
Increased extension of the knee
Elbow movement
Increased flexion of the wrist
Bending of the thumb at 90 degrees
Hyper mobility syndrome can be
Benign
Associated with the Ehlers- Danlos syndrome (EDS)
Benign hyper mobility syndrome can present with symptoms and signs of the disease i.e. pain, tiredness. This can also be mistaken as being double jointed. One in 10,000 may suffer with this condition. Does the Sri Lankan record breaking off spinner suffer from the hyper mobility syndrome i.e. double jointed? It would be interesting to know.
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a group of genetic disorders that affect the connective tissues in the body, which results in decreased collagen formation in the body. These provide strength and elasticity to the body structure. Mainly the tendons and ligaments are affected. The genetic disorder is due to gene mutation. The disease can be regular EDS or Vascular EDS. Severe symptoms with regular EDS or vascular EDS can have debilitating symptoms of pain which stops the sufferers from work. In the United Kingdom these patients may benefit from disability allowances. Therefore, treating and managing these patients would be challenging.
Ehlers-Danlos can also affect the skin, joints, and blood vessel walls. The syndrome is characterised by extremely flexible joints and very stretchy, fragile skin.
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a severe form of the syndrome and affects the blood vessels in the body as stated earlier. The fragile skin can bruise easily. The organs can be affected including the heart.
There is no cure for EDS but symptoms can be treated and controlled.
Diagnosis
Clinical symptoms and signs such as increased bending of
joints as in the diagram.
Skin test
Family history
Investigations such as echocardiogram to check the heart
CT and MRI scans
Biopsy of skin to see abnormal collagen
Treatment
Manage the pain effectively. Visit a pain clinic i.e. consult a
specialist in pain medicine
Exercises to strengthen the muscles
Walking, swimming, mild exercises
Calcium and vitamin D supplements
Manage pregnancy with care in women
Avoid contact sports like Rugby
Management of pain
Simple analgesics
Paracetamol, NSAIDS. COX 2 inhibitors
Moderate analgesics
Codeine Phosohate
Strong Analgesins
Opiate patches such as Fentanyl
Bupronorphine
Physiotherapy
Acupuncture
Cognitive behavioural therapy
Interventions – Trigger point injections, etc.
Dr Senasinghe MBBS, Dip in Pain Med, FFARCS, FFPMCA, CCST(U.K) is a Consultant in pain medicine (United Kingdom and Sri Lanka) at the ‘London Pain Management Centre’ No 31, Horton Place, Colombo 7, Sri Lanka (hotline 0767155716). Dr Senasinghe has 25 year’s experience as a doctor in the UK of which 18 years are as a Consultant in pain medicine at the NHS UK.
